Reasoning quiz is to judge your mental as well as your logical ability of thinking, how sharply you think and make an effective decision on a given situation.This reasoning quiz enhances your preparation for upcoming examination and evaluates your performance. So, do practice on regular basis and increase your selection chances in upcoming examinations. Reasoning section is more scoring section for all in several Banking exams if you have a right approach of decision making for solving the problem.
Mahendra Guru provides you Reasoning Quiz for Bank examination based on the latest pattern. So you can do practice on the regular basis, it will definitely help you to score marks in the exam. Reasoning is the most important section for all the govt exam like IBPS PO/ Clerk/SO/RRB RBI, SBI Clerk, Insurance, SSC-MTS, CGL, CHSL, State Level and other Competitive exams.
Q.1-5. Study the following information carefully to answer the questions given below.
In an examination, six subjects A, B, C, D, E and F were available for a candidate of which only three had to be offered under the following conditions:
1. One who offered A had to offer B also.
2. One who offered A could not offer E.
3. One who offered C or D could not offer F.
The distribution of the candidates over the subjects was as follows:
A – 70, B – 70, C – 90, D – 85, E – 70, F – 35.
निम्नलिखित सूचनाओं को ध्यानपूर्वक अध्ययनकर नीचे दिये गये प्रश्नों के उत्तर दीजिये।
एक परीक्षा में छः विषय A, B, C, D, E और F एक उम्मीदवार के लिए उपलब्ध है, जिनमें से केवल तीन निम्न शर्तों के अंतर्गत प्रस्तावित किये जाते हैं।
1. एक जो A का प्रस्ताव रखता है B का भी हमेशा प्रस्ताव क्रमशः रखता है।
2. एक जो A का प्रस्ताव रखता है, E का प्रस्ताव नहीं रख सकता है।
3. एक जो C या D का प्रस्ताव रखता है, F के साथ प्रस्ताव, नहीं रख सकता है।
विषयों के अनुसार उम्मीदवारों का वितरण निम्न रूप में से किया गया है।
A – 70, B – 70, C – 90, D – 85, E – 70, F – 35
Q.1. How many combinations were permitted?
01. Four
02. Five
03. Six
04. Seven
05. None of these
कुल कितने प्रकार के संयोजन स्वीकार किये जायेंगे?
01. चार
02. पांच
03. छः
04. सात
05. इनमें से कोई नहीं
Q.2. How many candidates appeared for the examination in all?
01. 120
02. 130
03. 140
04. 380
05. None of these
सभी में, परीक्षा के लिए कुल कितने उम्मीदवार उपस्थित हुए?
01. 120
02. 130
03. 140
04. 380
05. इनमें से कोई नहीं
Q.3. How many candidates offered the combination A + B + C?
01. 15
02. 20
03. 35
04. 70
05. None of these
A + B + C के संयोजन का कुल कितने उम्मीदवारों ने प्रस्ताव रखा?
01. 15
02. 20
03. 35
04. 70
05. इनमें से कोई नही
Q.4. How many candidates combined C with D?
01. 15
02. 20
03. 35
04. 70
05. None of these
कितने उम्मीदवारों ने C का D के साथ संयोजन किया ?
01. 15
02. 20
03. 35
04. 70
05. इनमें से कोई नही
Q.5. How many candidates offered B with F?
01. 15
02. 20
03. 35
04. 70
05. None of these
कितने उम्मीदवारों ने B का F के साथ संयोजन किया ?
01. 15
02. 20
03. 35
04. 70
05. इनमें से कोई नही
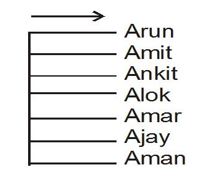
Q.6-10. Study the following information carefully and answer the question given below.
(i) Aman, Arun, Ajay, Amar, Amit, Alok and Ankit are sitting on a wall and all of them are facing towards east.
(ii) Ajay is immediate to the right of Amar.
(iii) Arun is at an extreme end and Amit is his neighbour.
(iv) Ankit is between Amit and Alok.
(v) Amar sits third from the south end.
निम्नलिखित जानकारी का ध्यानपूर्वक अध्ययन करें और नीचे दिये गये प्रश्नों के उत्तर दीजिए-
(i) अमन, अरून, अजय, अमर, अमित, आलोक और अंकित एक दीवार पर बैठे है और सभी पूर्व की ओर देख रहे हैं।
(ii) अजय, अमर के तुरन्त दायें है।
(iii) अरून, एक अन्तिम छोर पर है और अमित उसका पड़ोसी हैं।
(iv) अंकित, अमित और आलोक के बीच में है।
(v) अमर, दक्षिण छोर से तीसरा बैठा है।
Q.6. Who sits immediate to the right of Amit?
(1) Aman
(2) Ajay
(3) Amar
(4) Alok
(5) Ankit
अमित के तुरन्त दायें कौन बैठा हैं?
(1) अमन
(2) अजय
(3) अमर
(4) आलोक
(5) अंकित
Q.7. Which of the following pairs of people sit at the extreme ends?
(1) Aman, Arun
(2) Aman, Amit
(3) Ajay, Arun
(4) Alok, Arun
(5) Cannot be determined
निम्न में कौन से व्यक्तियों का समूह अन्तिम छोरों पर बैठा है?
(1) अमन, अरून
(2) अमन, अमित
(3) अजय, अरून
(4) आलोक, अरून
(5) तय नहीं कर सकते
Q.8. Ajay should interchange his place from which person to get the third position from the north end?
(1) Amit
(2) Alok
(3) Ankit
(4) Amar
(5) Aman
उत्तर छोर से तीसरा स्थान प्राप्त करने के लिए अजय को किस व्यक्ति के साथ अपना स्थान परिवर्तित करना चाहिए?
(1) अमित
(2) आलोक
(3) अंकित
(4) अमर
(5) अमन
Q.9. Which of the following pairs of people is the neighbour of Amar?
(1) Aman, Ajay
(2) Aman, Alok
(3) Ajay, Amit
(4) Ajay, Alok
(5) Cannot be determined
निम्नलिखित में से कौन-से व्यक्तियों का जोड़ा अमर का पड़ोसी है?
(1) अमन, अजय
(2) अमन, आलोक
(3) अजय, अमित
(4) अजय, आलोक
(5) तय नहीं कर सकते
Q.10. Which of the following conditions is not required to find out the place of Aman?
(1) (i)
(2) (ii)
(3) (iii)
(4) (iv)
(5) None of these
अमन के स्थान को ज्ञात करने के लिए निम्न में से किस शर्त की आश्यकता नहीं है?
(1) (i)
(2) (ii)
(3) (iii)
(4) (iv)
(5) इनमें से कोई नहीं
ANSWER
Q.1. (1) According to the given conditions there should be four possible combinations – ABC, ABD, ABF, CDE.
दी गई शर्तों के अनुसार, चार सम्भावित संयोजन होने चाहिए। - ABC, ABD, ABF, CDE हैं।
Q.2. (3) The possible combinations are – ABC, ABD, ABF, CDE. E is only in CDE.
So, number of candidates who offered CDE = number of candidates who offered E = 70.
F is there only in ABF. So, number of candidates who offered ABF = number of candidates who offered F = 35.
D is there in ABD and CDE. So, Number of candidates who offered ABD = number of candidates who offered D – number of candidates who offered CDE = 90 – 70 = 20.
Hence, total number of candidates appeared = 70 + 35 + 15 + 20 = 140
सम्भावित संयोजन ABC, ABD, ABF, CDE हैं। E केवल CDE में हैं। अतः उम्मीदवारों की संख्या जो CDE का प्रस्ताव करते हैं = उम्मीदवारों की संख्या जो E का प्रस्ताव करते हैं = 70 F केवल ABF में है अतः उम्मीदवारों की संख्या जो ABF का प्रस्ताव करते हैं = उम्मीदवारों की सख्ंया जो F का प्रस्ताव करते हैं = 35 D, ABD और CDE में है अतः उम्मीदवारों की संख्या जो ABD का प्रस्ताव करते हैं = उम्मीदवारेां की संख्या जो D का प्रस्ताव करते हैं उम्मीदवारेां की संख्या जो CDE का प्रस्ताव करते हैं = 90 – 70 = 20 अतः उपस्थित हुए कुल उम्मीदवारों की संख्या = 70 + 35 + 15 + 20 = 140
Q.3. (2) Number of candidates who offered ABC = 90-70 = 20
उम्मीदवारों की संख्या जो ABC का प्रस्ताव करते हैं 90-70 = 20
Q.4. (4) Clearly, required number of candidates= number of candidates who offered CDE = 70.
उम्मीदवारों की आवश्यक संख्या = उम्मीदवारों की संख्या जो CDE का प्रस्ताव करते हैं = 70
Q.5. (3) Required number of candidates = number of candidates who offered ABF = 35.
उम्मीदवारों की आवश्यक संख्या = उम्मीदवारों की संख्या जो ABF का प्रस्ताव करते हैं = 35
Q.6-10.
Q.6. (5) Q.7. (1) Q.8. (3) Q.9. (4) Q.10. (5)