Dear Readers,
As SSC MTS | CHSL notification is out and candidates have started their preparation for this exam. Mahendras also has started special quizzes for this examination. This series of quizzes are based on the latest pattern of the SSC MTS | CHSL examination. Regular practice of the questions included in the quizzes will boost up your preparations and it will be very helpful in scoring good marks in the examination.
Q- 1 If 3 men and 4 boys can do a piece of work in 6 days and 6 men and 3 boys can do it in 4 days. Compare the efficiency of a man to that of a boy.
A. 1:1
B. 2:1
C. 1:2
D. 3:1
यदि 3 आदमी और 4 लड़के कार्य के एक भाग को 6 दिनों में पूरा कर सकते हैं तथा 6 आदमी और 3 लड़के इसे 4 दिनों में पूरा कर सकते हैं। एक आदमी की कार्यक्षमता की एक लड़के की कार्यक्षमता से तुलना कीजिए।
A. 1:1
B. 2:1
C. 1:2
D. 3:1
Q-2 An article has marked price of Rs. 7600 and is available at a discount of 15%. The shopkeeper gives another discount to the buyer and sells the article for Rs. 5814. What is the second discount (in %) offered?
A. 20
B. 10
C. 12.5
D. 15
एक वस्तु का अंकित मूल्य 7600 रुपये है और 15% की छूट पर उपलब्ध है। दुकानदार, खरीददार को एक और छूट देता है और वस्तु 5814 रुपये में बेचता है। दूसरी दी गई छूट (% में) कितनी है?
A. 20
B. 10
C. 12.5
D. 15
Q-3
If
 , find the value of
, find the value of  .
. A. ± 1
B. 1
C. 9
D. 4
यदि
 , तो
, तो  का मान ज्ञात कीजिये।
का मान ज्ञात कीजिये। A. ± 1
B. 1
C. 9
D. 4
Q-4
If (a6 – b6) = 8(a4 + b4 + a2b2), , then find the value of (a2 – b2)..
A. 2
B. 4
C. 8
D. 16
यदि (a6 – b6) = 8(a4 + b4 + a2b2), है, तो (a2 – b2).का मान ज्ञात कीजिए।
A. 2
B. 4
C. 8
D. 16
Q-5 The average marks of 20 students in a test is 75. Later it is found that three marks 53, 60 & 76 were wrongly entered as 93, 64 & 86. The average marks after mistakes were rectified is
A. 72.3
B. 72.2
C. 71.6
D. 71.8
एक परीक्षा में 20 छात्रों के औसत अंक 75 है। बाद में यह पाया गया कि तीन अंक 53, 60 & 76 को गलत तरह से 93, 64& 86 के रूप में लिखा गया। गलतियों को सुधारने के बाद औसत अंक है
A. 72.3
B. 72.2
C. 71.6
D. 71.8
Q-6 In ∆PQR, S and T are the points on PQ and PR respectively, such that ST ǁ QR and PS ∶ SQ = 3 ∶ 5, PR = 6 CM, then PT is :
A. 2 cm
B. 2.25 cm
C. 3.5 cm
D. 4 cm
∆PQR में, S और T क्रमशः PQ और PR पर बिंदु इस प्रकार हैं, कि ST ǁ QR और PS ∶ SQ = 3 ∶ 5, PR = 6 सेमी, तब PT का मान क्या है?
A. 2 सेमी
B. 2.25 सेमी
C. 3.5 सेमी
D. 4 सेमी
Q-7 The perimeter and the length of one of the diagonals of a rhombus is 34 cm and 8 cm respectively. Find the length of its other diagonal (in cm).
A. 7.5
B. 30
C. 22.5
D. 15
एक सम चतुर्भुज का परिमाप और उसके विकर्णों में से एक विकर्ण की लम्बाई क्रमशः 34 सेमी और 8 सेमी है। उसके अन्य विकर्ण (सेमी में) की लम्बाई ज्ञात कीजिये।
A. 7.5
B. 30
C. 22.5
D. 15
Q-8 An article is sold at a discount of 25% and an additional discount of 12% is allowed on payment in cash form. If Suparna purchased the article by paying Rs. 2112 in cash, the market price of the article value is?
A. 2860
B. 3250
C. 4400
D. 3200
एक वस्तु को 25 प्रतिशत की छूट पर बेचा जाता है और नगद भुगतान करने पर 12 प्रतिशत की अतिरिक्त छूट दी जाती है। यदि सुपर्णा 2112 रुपए का नगद भुगतान करके वस्तु खरीदती है, तो उस वस्तु का अंकित मूल्य क्या है?
A. 2860
B. 3250
C. 4400
D. 3200
Q-9 If the price of sugar is decreased by 18%, then a person can buy 16.2 kg sugar more for Rs. 4500. What will be the new price (in Rs) of sugar per kg?
A. 40
B. 60
C. 45
D. 50
यदि चीनी का मूल्य 18% कम होता है, तो एक व्यक्ति 4500 रुपये में 16.2 किग्रा अधिक चीनी खरीद सकता है। चीनी का प्रति किग्रा नया मूल्य (रुपये में) क्या होगा?
A. 40
B. 60
C. 45
D. 50
Q-10 A shopkeeper sold 14 pieces of a pen for Rs. 2700 and his profit is equal to the cost price of 4 pieces of the pen. Find the difference between the selling price and the cost price of 14 pieces of the pen?
A. 600
B. 800
C. 900
D. 700
एक दुकानदार ने 2700 रुपये में 14 कलम बेचे और उसका लाभ 4 कलमों के क्रय मूल्य के बराबर है। 14 कलमों के विक्रय मूल्य और क्रय मूल्य के बीच का अंतर ज्ञात कीजिए।
A. 600
B. 800
C. 900
D. 700
ANSWER KEY -----------
Suppose the efficiency of a man = x/day
Efficiency of a boy = y/ day
According to problem,
⇒ (3x + 4y) × 6 = (6x + 3y) × 4
⇒ 18x + 24y = 24x + 12y
⇒ 6x = 12y
⇒ x ∶ y = 2 ∶ 1
∴ Ratio of efficiency of a man to that of a boy = 2 ∶ 1
मान लीजिये कि एक आदमी की कार्यक्षमता = x/दिन
एक लड़के की कार्यक्षमता = y/ दिन
प्रश्नानुसार,
⇒ (3x + 4y) × 6 = (6x + 3y) × 4
⇒ 18x + 24y = 24x + 12y
⇒ 6x = 12y
⇒ x ∶ y = 2 ∶ 1
∴ एक आदमी की कार्यक्षमता का एक लड़के की कार्यक्षमता से अनुपात = 2 ∶ 1
Q-2(2)
Given,
MP = 7600
Initial SP after 15% discount = 7600 - (0.15 × 7600) = 6460
Final SP after x% discount = 5814 = 6460 - 0.01x × 6460
⇒ 64.6x = 646
∴ x =
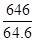 = 10%
= 10% दिया हुआ,
MP = 7600
15% छूट के बाद प्रारंभिक SP = 7600 - (0.15 × 7600) = 6460
अंतिम SP x% छूट के बाद = 6460 - 0.01x × 6460
⇒ 64.6x = 646
∴ x =
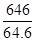 = 10%
= 10% Q-3(1)
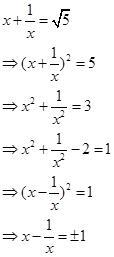
Q-4(3)
(a2 – b2) = (a + b)(a – b)
We can write, (a6 – b6) = (a2 – b2)(a4 + b4 + a2b2)
⇒ (a2 – b2)(a4 + b4 + a2b2) = 8(a4 + b4 + a2b2)
⇒ (a2 – b2) = 8
(a2 – b2) = (a + b)(a – b)
हम लिख सकते है, (a6 – b6) = (a2 – b2)(a4 + b4 + a2b2)
⇒ (a2 – b2)(a4 + b4 + a2b2) = 8(a4 + b4 + a2b2)
⇒ (a2 – b2) = 8
Q-5(1)
Average marks of 20 students = 75
∴ Total marks of 20 students = 20 × 75 = 1500
∴ Actual total marks of 20 students,
⇒ 1500 – (93 + 64 + 86) + (53 + 60 + 76)
⇒ 1500 – 243 + 189
⇒ 1446
∴ Average marks of 20 students =
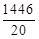 = 72.3
= 72.3 20 छात्रों के औसत अंक = 75
∴ 20 छात्रों के कुल अंक = 20 × 75 = 1500
∴ 20 छात्रों के वास्तविक कुल अंक,
⇒ 1500 – (93 + 64 + 86) + (53 + 60 + 76)
⇒ 1500 – 243 + 189
⇒ 1446
∴ 20 छात्रों के औसत अंक=
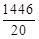 = 72.3
= 72.3 Q-6(2)
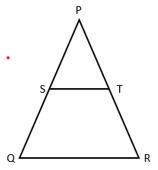

In ∆PST and PQR,
Given, ST ǁ QR intersected by a transversal PQ.
⇒ ∆PST ~ ∆PQR
⇒ PS ∶ SQ = PT ∶ RT
⇒ PT ∶ RT = 3 ∶ 5
⇒ PT ∶ (PT + RT) = 3 ∶ 8
⇒ PT = 6 × 3/8
∴ PT = 2.25 cm
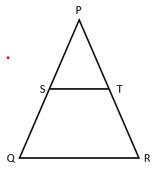
∆PST और PQR में,
दिया है, ST ǁ QR अनुप्रस्थ PQ के द्वारा प्रतिच्छेदित हैं।
⇒ ∆PST ~ ∆PQR
⇒ PS ∶ SQ = PT ∶ RT
⇒ PT ∶ RT = 3 ∶ 5
⇒ PT ∶ (PT + RT) = 3 ∶ 8
⇒ PT = 6 × 3/8
∴ PT = 2.25 सेमी
Q-7(4)
Let d1 is the first diagonal and d2 is the second diagonal.
Perimeter of rhombus = 34
Side of the rhombus (a) = 34/4 = 8.5 cm
First diagonal d1 = 8 cm
Now,
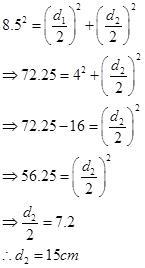
माना, पहला विकर्ण d1 है और दूसरा विकर्ण d2 है
सम चतुर्भुज का परिमाप = 34
सम चतुर्भुज (a) की भुजा = 34/4 = 8.5 सेमी
पहला विकर्ण d1 = 8 सेमी
अब,
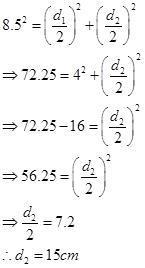
Q-8(4)
Let the market price of the article be Rs. x.
Now according to the question, we can write,
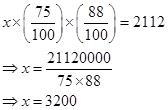
∴ The marked of the article = Rs. 3200.
माना वस्तु का अंकित मूल्य x रुपए है
अब, प्रश्न के अनुसार हम लिख सकते हैं,
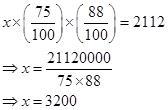
∴ वस्तु का अंकित मूल्य = 3200 रुपए
Q-9(4)
Q-9(4)
then the new price per kg of article =
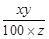
So, x = 18%, y = 4500, & z = 16.2 kg
∴ New price per kg =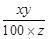 =
= 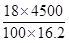 = 50
= 50
यदि वस्तु के मूल्य में x% की कमी होती है और खरीददार y रुपये में z किग्रा अधिक चीनी प्राप्त करता है वस्तु का प्रति किग्रा नया मूल्य =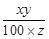
∴ New price per kg =
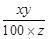 =
= 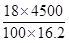 = 50
= 50 यदि वस्तु के मूल्य में x% की कमी होती है और खरीददार y रुपये में z किग्रा अधिक चीनी प्राप्त करता है वस्तु का प्रति किग्रा नया मूल्य =
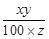
तो, x = 18%, y = 4500, तथा z = 16.2 किग्रा
∴ प्रति किग्रा नया मूल्य =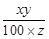 =
= 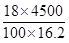 = 50
= 50
∴ प्रति किग्रा नया मूल्य =
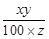 =
= 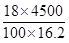 = 50
= 50 Q-10(1)
Let the cost price of 1 piece of pen be x
So, the cost price of 4 pieces of pen = 4x
And the cost price of 14 pieces of pen = 14x
The selling price of 14 pieces of pen = Rs. 2700
According to the question ∶
14x + 4x = 2700
⇒ x = 150
The cost price of 1 piece of pen = Rs. 150
So, the cost price of 14 pieces of pen = 14 × 150 = 2100
Required difference = 2700 – 2100 = Rs. 600.
माना 1 कलम का क्रय मूल्य x रुपये है।
इस प्रकार, 4 कलमों का क्रय मूल्य = 4x
और 14 कलमों का क्रय मूल्य = 14x
14 कलमों का विक्रय मूल्य = 2700 रुपये
प्रश्नानुसार ∶
14x + 4x = 2700
⇒ x = 150
1 कलम का क्रय मूल्य = 150 रुपये
इस प्रकार, 14 कलमों का क्रय मूल्य = 14 × 150 = 2100 रुपये
आवश्यक अंतर = 2700 – 2100 = 600 रुपये





0 comments:
Post a Comment
MAHENDRA GURU